Understanding Reliability Engineering

In an operational environments such as a refinery, chemical plant, or some other type of heavy processing facility, Reliability Engineering (RE) is far more than a technical function.
It is a core business philosophy and a disciplined engineering practice that ensures physical assets perform their required functions, without failure, within their intended operating context, throughout their entire lifecycle.
In these industries, reliability is synonymous with predictable, low‑cost and safe production. It is the proactive, data‑driven backbone that links maintenance excellence, operational discipline, safety integrity and profitability.
What Reliability Engineering Is Identified As: A Strategic Imperative.
In capital‑intensive industrial operations, Reliability Engineering is recognized as:
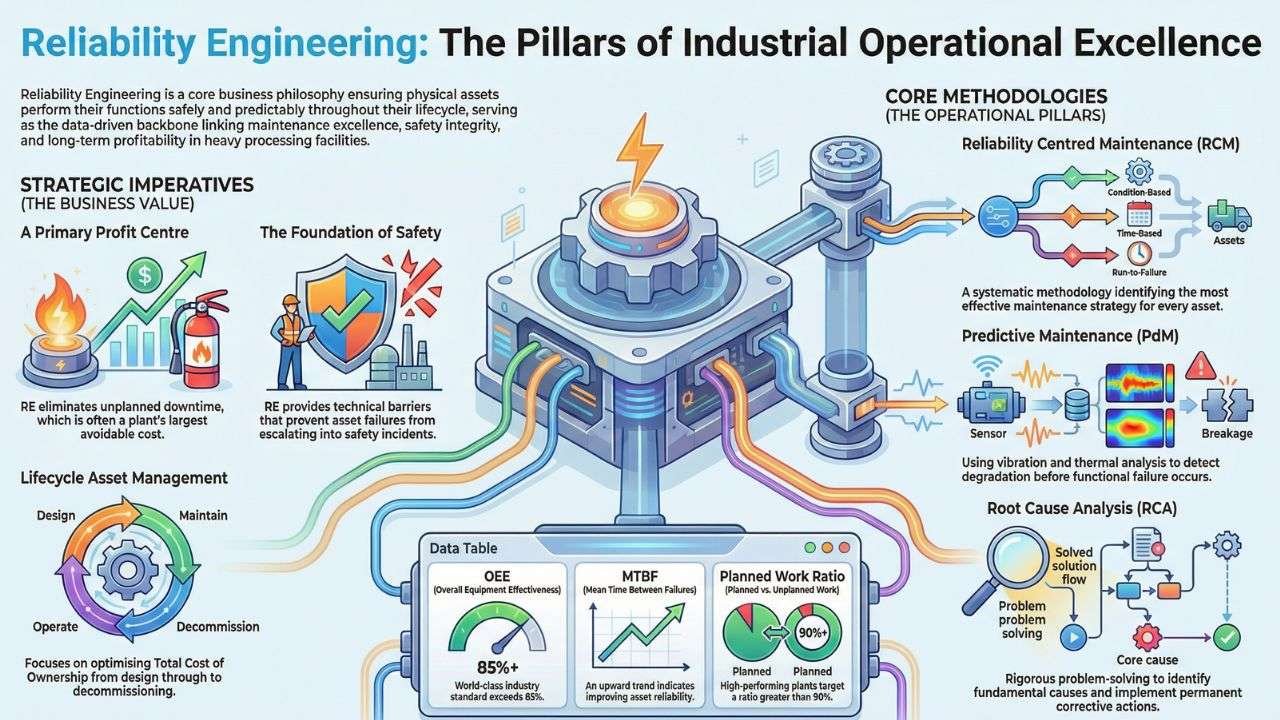
- A Primary Profit Centre: Unplanned downtime is often the largest avoidable cost in a plant. RE is the systematic mechanism for eliminating it through failure prevention, early detection and disciplined planning.
- The Foundation of Safety: Most catastrophic safety incidents originate from asset integrity failures. RE provides the technical barriers, design, monitoring and maintenance, that prevent these failures from escalating into safety events.
- A Risk Management Function: RE quantifies and mitigates the likelihood and consequences of asset failure. It transforms risk from an abstract concept into measurable, actionable engineering controls.
- Lifecycle Asset Management: Rather than focusing on day‑to‑day firefighting, RE optimizes the total cost of ownership (TCO) from design and procurement through operation, modification and eventual decommissioning.
How Reliability Is Pursued: A Multi‑Faceted Discipline.
Reliability Engineering is a structured, relentless pursuit built on several core pillars:
- Reliability‑Centred Maintenance (RCM): A systematic methodology that identifies asset functions, failure modes and the most effective maintenance strategy, reactive, preventive, predictive, or proactive. RCM answers the fundamental question, “What must be done to ensure this asset continues to perform its intended function?”
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and FMEA: When failures occur, RE applies rigorous problem‑solving tools, 5 Whys, Cause‑and‑Effect diagrams, FMEA and formal FRACAS systems, to identify fundamental causes and implement permanent corrective actions.
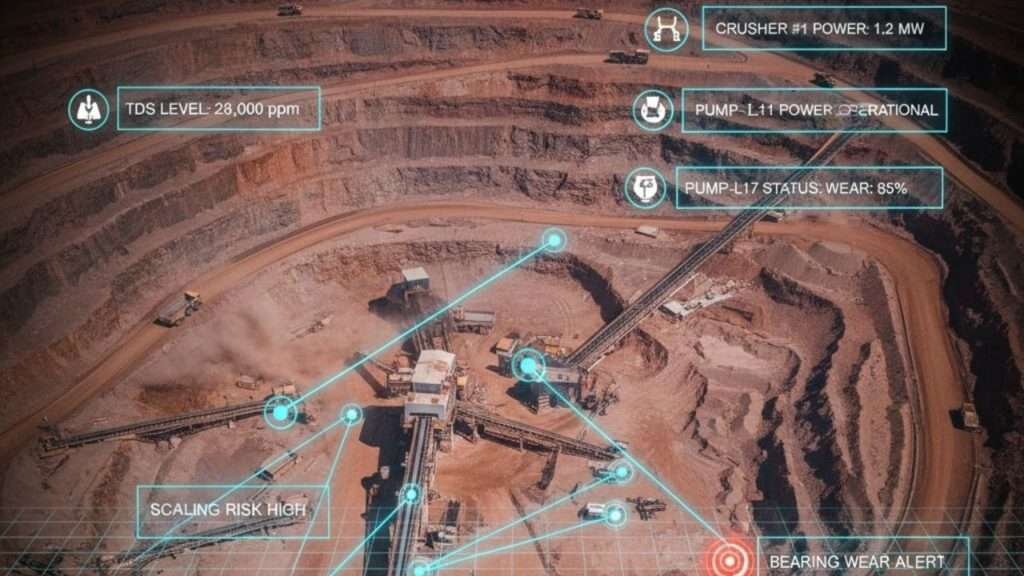
- Predictive Maintenance (PdM) and Condition Monitoring: The cornerstone of modern reliability. Technologies such as vibration analysis, thermography, ultrasonic testing, oil analysis and motor circuit analysis detect early signs of degradation, enabling planned intervention long before functional failure.
- Asset Performance Management (APM): APM integrates analytics, KPIs and risk models to provide a real‑time, holistic view of asset health and performance. It enables prioritization based on criticality, risk exposure and business impact.
- Defect Elimination: A proactive program targeting chronic, recurring issues that erode capacity, increase energy consumption, or inflate corrective maintenance. Eliminating small defects prevents large failures.
- Spare Parts & MRO Strategy: Reliability engineers define critical spares, optimize inventory levels and qualify suppliers to ensure part quality and availability support asset reliability rather than undermine it.
How Performance Is Measured: Metrics That Matter.
Reliability performance is tracked through a hierarchy of metrics that cascade from executive dashboards to frontline teams:
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): The gold standard for quantifying productive manufacturing time.
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality: World‑class OEE in heavy industry typically exceeds 85%.
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): Measures average operating time between failures. An upward trend indicates improving reliability.
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR): Measures the average time required to restore an asset to service. Lower MTTR reflects better maintainability, planning and execution.
- Planned vs. Unplanned Work Ratio: A cultural and operational indicator. High‑performing plants target >90% planned work, as unplanned work is typically around 2 to 3 times more expensive.
- Maintenance Cost as a Percentage of Replacement Asset Value (RAV): A high‑level financial benchmark for maintenance efficiency and asset stewardship.
- Reliability & Risk KPIs: Examples include: Number of critical equipment trips, Failures of safety‑critical devices, Proof‑testing backlog and Safety incidents linked to equipment failure. These metrics connect reliability performance directly to operational and safety outcomes.
Teaching the Workforce: Building a Culture of Reliability.
Reliability is not the exclusive domain of engineers. It requires plant‑wide engagement and shared ownership. This culture is built through:
Operator‑Driven Reliability (ODR).
Operators are the first line of defence. ODR programs train them to:
- Conduct basic condition monitoring using senses and simple tools.
- Operate equipment within precise parameters to avoid induced stress.
- Report abnormalities promptly and accurately into the CMMS.
Formal Training Programs.
From foundational “Reliability 101” courses for all staff to advanced certifications for specialists in vibration analysis, lubrication, or RCA facilitation.
Visual Management & Communication.
Dashboards in control rooms and maintenance shops display real‑time OEE, top loss reasons and reliability KPIs. Successes, such as MTBF improvements or predicted failures averted, are celebrated to reinforce desired behaviours.
Cross‑Functional Teams.
Operators, maintainers and reliability engineers collaborate on RCAs, improvement projects and strategy reviews. This breaks down silos and builds shared understanding of asset behaviour and risk.
The Role of the Reliability Engineer: The Technical Conductor.
Reliability engineers are analysts, influencers and long‑term strategists. Their responsibilities include:
- Analysing asset data to identify bad actors and emerging failure patterns.
- Facilitating RCAs and FMEAs with cross‑functional teams.
- Developing and optimizing maintenance strategies using RCM principles.
- Managing PdM technologies and interpreting condition monitoring results.
- Reviewing capital projects to ensure inherent reliability and maintainability.
- Reporting performance and translating technical insights into business risk and opportunity.
They orchestrate the technical, operational and financial elements of asset reliability.
The Digital Enabler: CMMS/EAM, ERP and AI.
Modern Reliability Engineering is powered by a digital ecosystem that integrates execution, business context and advanced analytics.
CMMS/EAM: The Foundational Data Hub.
- Single Source of Truth: Consolidates work history, failure codes, parts usage, labour hours and costs.
- Workflow Engine: Automates PdM work orders, enforces maintenance plans and tracks RCA actions.
- Condition Monitoring Integration: Ingests PdM data directly into asset records, triggering alerts and work orders.
- Lifecycle Tracking: Links manuals, warranties and specifications to asset records for informed decision‑making.
ERP: The Business Context.
- Financial Justification: Connects maintenance costs to production output and profitability.
- Inventory Optimization: Ensures critical spares availability without excessive capital tie‑up.
- Integrated Planning: Aligns turnarounds, production schedules and financial budgets.
AI & Advanced Analytics: The Cognitive Layer
AI transforms reliability from reactive to predictive and prescriptive:
- Predictive Failure Modelling: Machine learning identifies complex failure signatures and predicts time‑to‑failure.
- Prescriptive Recommendations: Systems propose optimal intervention windows, required parts and procedures.
- Root Cause Suggestion: AI analyses historical data to propose likely root causes for new failure patterns.
- Digital Twins: Virtual models simulate asset behaviour and test operational changes before implementation.
- NLP for Unstructured Data: AI extracts insights from technician notes, operator logs and inspection reports.
Conclusion: The Reliable Path Forward.
Reliability Engineering represents the evolution from reactive maintenance to a proactive, data‑driven science of asset management.
It is pursued through rigorous methodologies like RCM and RCA, measured through metrics such as OEE and MTBF and embedded into the workforce through ODR and continuous training.
The modern reliability ecosystem, anchored by CMMS/EAM for execution, ERP for business context (although some ERP’s such as SAP do have extensive asset management functionality) and AI for predictive intelligence, transforms intuition into insight, reactions into predictions and maintenance departments into value creators.
Plants that embrace this approach achieve predictable operational excellence, where safety and productivity are not competing priorities but natural outcomes of a fundamentally reliable operation.