Work Execution Preparation Process

In heavy industrial, mining, processing and manufacturing environments, the quality of maintenance execution is determined long before a technician arrives at the job site.
The world’s best organisations understand that preparation is not a clerical task, it is a strategic capability.
When preparation is structured, disciplined and aligned with operational realities, maintenance work becomes safer, faster, more predictable and dramatically more effective.
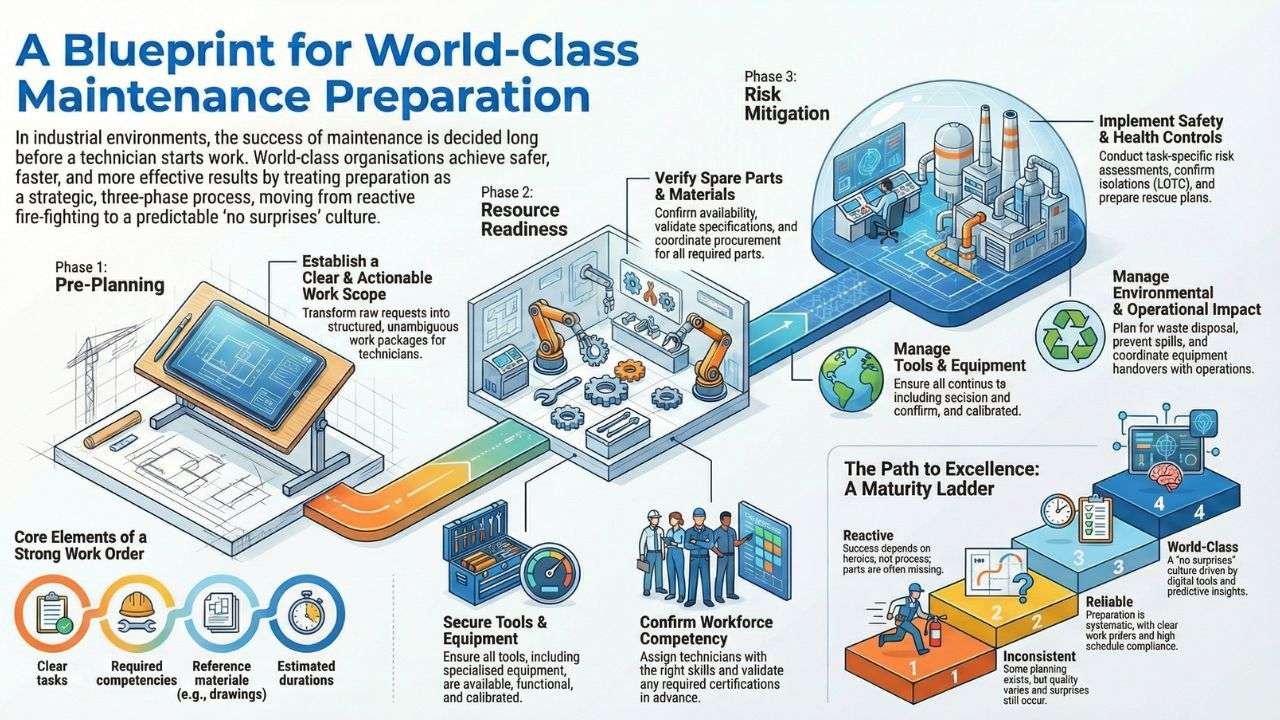
With the above in mind, let’s look at a three‑phase framework grounded in global best practice: Pre‑Planning, Resource Readiness and Risk Mitigation.
Combined with digital enablement, industry‑specific insights and a maturity model, this framework helps organisations build the world’s highest‑quality Work Execution Preparation Processes.
Phase 1: Pre‑Planning, Establishing a Clear and Actionable Work Scope.
Every world‑class maintenance job begins with a well‑defined work order.
Pre‑Planning is where planners transform raw requests into structured, actionable work packages that technicians can execute without ambiguity.
Core Elements of Pre‑Planning:
- Clear task descriptions outlining what must be done and why.
- Defined responsibilities and required competencies.
- Reference materials such as drawings, manuals, SOPs and asset history.
- Estimated durations based on realistic task analysis.
- Operational coordination to confirm shutdown windows or production impacts.
A strong work order is the foundation for everything that follows. Without clarity at this stage, even the most skilled technicians will struggle.
Industry‑Specific Contrasts:
- Vehicle manufacturing: Pre‑Planning must consider takt‑time constraints, precision torque specifications and repeatability.
- Nickel acid/leach processing: Requires corrosion‑rate data, chemical isolation procedures and metallurgical considerations.
- Mining (iron ore, coal): Harsh dust environments and long travel distances demand detailed scoping to avoid return trips.
Building on a solid work order foundation, the next layer of preparation ensures no surprises (as much as possible).
Phase 2: Resource Readiness, Ensuring Everything Is Available & Verified.
Once the work is clearly defined, the next phase ensures that every resource required for flawless execution is ready, available and validated.
This is where many organisations fall short, and where world‑class performers excel.
Spare Parts and Materials:
- Confirm availability of all required parts.
- Validate the planned parts, specifications and suitability/compatibility/correctness.
- Identify long‑lead or critical spares early and if coming from overseas, allow for extra time in customs etc, this means getting them on the way to your site as soon as possible, once you’ve are 100% certain of what you are ordering.
- Coordinate procurement or supplier engagement, engage additional (contract) resources as required for highly critical events.
Tools and Equipment.
- Ensure tools and support equipment (including special tooling) are available, functional/fit-for-use and calibrated (if required).
- Reserve any special tooling & specialised equipment well in advance such as: torque multipliers, huck bolts & related tools, EWP’s, Scissor Lifts, Cranes that you don’t often use, lift and shift devices/equipment, NDT tools, especially the rare equipment, specialized drones or Magnetic Crawlers/Robotic Crawlers for Tank/Vessels.
- Confirm access to mobile equipment well in advance with the production team.
- Have as much of permit information as possible filled out in advance.
Workforce and Competency.
- Assign technicians with the right skills and experience and let people know what jobs they will be doing and on what days well in advance.
- Confirm contractor availability and suitablility (don’t take their word for it) and do all of this well in advance (they take holidays too).
- Validate certifications & competencies for high‑risk tasks well in advance.
Industry‑Specific Contrasts.
- Coal handling plants: Require specialised alignment tools for certain drive gearboxes and ,motors as well as some relatively unique equipment.
- Food manufacturing/industry: Needs sterile work environments to avoid contamination and post cleaning as well.
- Power generation: Requires highly specialised tools for turbine, boiler, or HV work.
Digital Enablement for World‑Class Preparation.
Use digital tools to prepare for maintenance to eliminate ambiguity, automate verification and improve accuracy but it’s also smart to prepare for the worse (hardware or software failure), so give that type of preparation some thought as well.
- Digital work packs with embedded drawings, marked up photos, GA Dwg’s, P&IDS, OEM details, special technical instructions/updates and isolation diagrams
- AI‑assisted parts verification that flags mismatches or obsolete components.
- Mobile planning apps for capturing field conditions.
- Digital isolation systems that reduce human error.
- Automated tool calibration alerts integrated with the work schedule.
- Predictive analytics recommending tasks based on condition data.
Digital enablement transforms preparation from a manual process into a precision‑driven, intelligence‑supported discipline.
With resources secured and validated, the final phase ensures that the work can be executed safely, responsibly and without exposing the organisation to unnecessary risk.
Phase 3: Risk Mitigation, Protecting People, Assets and the Environment.
Quality maintenance organisations treat risk mitigation as a non‑negotiable discipline. This phase ensures that all safety, health and environmental risks are identified, assessed and controlled before work begins.
Safety and Health Controls
- Conduct task‑specific risk assessments.
- Confirm isolation requirements (LOTO).
- Identify confined space, hot work, or working‑at‑heights hazards.
- Prepare rescue plans where required.
- Validate PPE requirements.
- Have any SCBA or External Breathing Equipment inspected, tested and available well in advance.
Environmental Considerations.
- Plan for waste disposal.
- Prevent contamination or spills.
- Minimise emissions, noise, or dust.
- Comply with environmental permits and site‑specific controls.
Operational Risk.
- Confirm production impacts.
- Coordinate with operations for equipment handover.
- Validate interlocks, alarms and protections.
Industry‑Specific Contrasts.
- Hydrometallurgical plants: Require chemical & gas neutralisation plans and spill‑response readiness.
- Wind turbine maintenance: Must consider weather windows, remote‑site rescue and working‑at‑heights protocols.
- Food and beverage: Requires allergen controls, sanitation and contamination prevention.
The Work Execution Preparation Maturity Ladder.
This ladder helps organisations diagnose their current capability and chart a path toward excellence.
Level 1, Reactive Preparation.
Work orders are vague, parts are missing and technicians discover issues at the job site. Success depends on heroics, not process.
Level 2, Structured but Inconsistent.
Some planning exists, but quality varies by planner, shift, or department. Parts and tools are “usually” ready, but surprises still occur.
Level 3, Integrated and Reliable.
Work orders are clear, resources are validated, risks are assessed and schedule compliance is high. Preparation is systematic, not optional.
Level 4, World‑Class Preparation.
Digital tools, predictive insights and cross‑functional coordination create a “no surprises” environment. Preparation is a cultural value, not a task.
Implementing Preparation in Your Operation: A Quick Start Guide.
To help you embed this framework into your organisation, here are practical steps you can take immediately:
- Audit your current preparation process to identify gaps.
- Standardise your work order templates with scope, references and acceptance criteria.
- Build a Resource Readiness Checklist covering parts, tools and workforce.
- Strengthen your risk assessment practices with consistent methodologies.
- Pilot a digital planning tool to digitise one part of the process.
- Train planners and supervisors in the three‑phase model.
- Review and improve continuously using technician feedback.
Conclusion, Preparation as a Strategic Advantage.
Effective, Safe & Efficient Maintenance execution is built on high quality preparation.
By adopting a structured, phased approach, Pre‑Planning, Resource Readiness and Risk Mitigation, organisations eliminate surprises, reduce downtime and dramatically improve safety and reliability.
When supported by digital tools, industry‑specific insights and a maturity model that guides continuous improvement, preparation becomes more than a process.
It becomes a strategic advantage, a cultural hallmark and a defining feature of operational excellence.